Methyl Epi-Jasmonate (MEJ) Biosynthesis
We also have a similar system for natural methyl epi-jasmonate production. Methyl epi-jasmonate, one of the major fragrance contributors of jasmine and several other flowers, is also synthesized in plants from linolenic acid via lipoxygenase pathway.
Methyl epi-jasmonate is the stereoisomer responsible for fragrance and bioactivity among methyl jasmonate stereoisomers. Epi-jasmonic acid, a free acid of methyl epi-jasmonate, is the initial product to be synthesized in plants, but gradually isomerized into (-)-jasmonic acid. These free acids are further methylated by jasmonic acid methylytransferase.
Biosynthesis Pathway of Methyl Epi-Jasmonate
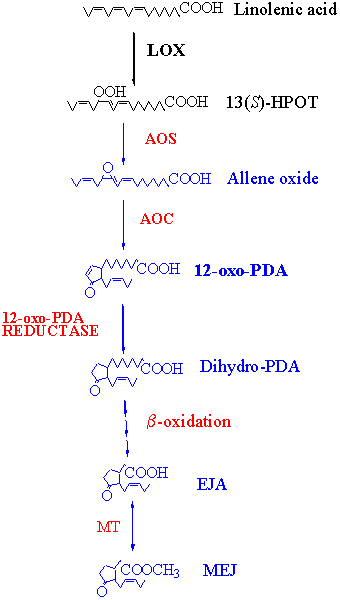
LOX: Lipoxygenase, HPOT: Hydroperoxy linolenic acid, AOS: Allene oxide synthase, AOC: Allene oxide cyclase, PDA: Phytodienoic acid, EJA: Epi-jasmonic acid, MT: Methyltransferase, MEJ: Methyl epi-jasmonate





