Forecasting
Forecasting
techniques (pg. 436 Exhibit 11.1)
1. Statistical (Time Series, Causal)
2. Judgement/Qualitative (Expert opinion, Market Survey, Delphi)
Time series analysis
1. Simple moving average
2. Weighted moving average
3. Exponential smoothing
4. Regression analysis
An Example
|
Month |
Demand |
3-month Moving Average |
3-month Wt. Moving Average (weights: 0.2, 0.3, 0.5) |
Exponential Smoothing (alpha = 0.1) |
|
1 |
650 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
700 |
|
|
0.1*650+0.9*650 = 650 |
|
3 |
810 |
|
|
0.1*700+0.9*650 = 655 |
|
4 |
800 |
(650+700+810)/3 = 720 |
0.2*650+0.3*700+0.5*810 = 745 |
0.1*810+0.9*655 = 670.5 |
|
5 |
900 |
(700+810+800)/3 = 770 |
0.2*700+0.3*810+0.5*800 = 783 |
0.1*800+0.9*670.5 = 683.5 |
|
6 |
700 |
(810+800+900)/3 = 837 |
0.2*810+0.3*800+0.5*900 = 852 |
0.1*900+0.9*683.5 = 705.2 |
|
7 |
|
(800+900+700)/3 = 800 |
0.2*800+0.3*900+0.5*700 = 780 |
0.1*700+0.9*705.2 = 704.7 |
Illustration
Pg.472 Problem 2
Exercise:
pg473 Problem 9
Forecasting errors
Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD) (pg.448)
An Example
|
Demand |
3-month Moving Average |
Deviation |
Absolute Deviation |
|
800 |
720 |
800-720 = 80 |
80 |
|
900 |
770 |
900-770 = 130 |
130 |
|
700 |
837 |
700-837 = -137 |
137 |
Sum of Absolute Deviation = 80+130+137 = 347
MAD = 347/3 = 115.7
|
Demand |
3-month Wt. Moving Average |
Deviation |
Absolute Deviation |
|
800 |
745 |
800-745 = 55 |
55 |
|
900 |
783 |
900-783 = 117 |
117 |
|
700 |
852 |
700-852 = -152 |
152 |
Sum of Absolute Deviation = 55+117+152 = 324
MAD = 324/3 = 108
|
Demand |
Exponential Smoothing |
Deviation |
Absolute Deviation |
|
800 |
670.5 |
800-670.5 = 129.5 |
129.5 |
|
900 |
683.5 |
900-683.5 = 216.5 |
216.5 |
|
700 |
705.2 |
700-705.2 = -5.2 |
5.2 |
Sum of Absolute Deviation = 129.5+216.5+5.2 = 351.2
MAD = 351.2/3 = 117.1
Hence, the 3-mth weighted moving average has the lowest MAD and is the best forecast method among the three.
Control limits for a range of MADs (Pg.450 Exhibit 11.11)
|
Number of MADs |
Accuracy |
|
+/- 1 |
57% |
|
+/- 2 |
88.9% |
|
+/- 3 |
98.3% |
|
+/- 4 |
99.9% |
With 57% accuracy, the forecast demand for July using 3-mth Wt. Moving Average = 780 +/- 108 (672 to 888)
With 88.9% accuracy, the forecast demand for July using 3-mth Wt. Moving Average = 780+/- 2*108 (564 to 996)
Exercise:
pg.471 Problem 3, 11
Assumptions
1. Linear -- the past data and future projections are fall about a
straight line (least squares method: minimize the sum of squared forecast
error)
2. Time is the independent variable, x
Y = a + bx
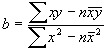
![]()
An example
|
|
Month (x) |
Profit (y) |
xy |
x2 |
|
|
1 |
31 |
31 |
1 |
|
|
2 |
40 |
80 |
4 |
|
|
3 |
30 |
90 |
9 |
|
|
4 |
34 |
136 |
16 |
|
|
5 |
25 |
125 |
25 |
|
|
6 |
20 |
120 |
36 |
|
Total |
21 |
180 |
582 |
91 |
|
Average |
3.50 |
30.00 |
97.00 |
15.17 |
b = (582-6*3.5*30)/(91-6*3.5*3.5) = -2.7
a = 30-(-2.7)*3.5 = 39.6
Y = 39.6 - 2.7x
Coding the time variable to simplify computation (i.e., ![]()
Case 1: odd number of time elements
|
Time |
Code |
|
January |
-2 |
|
February |
-1 |
|
March |
0 |
|
April |
1 |
|
May |
2 |
Case 2: even number of time elements
|
Time |
Code |
|
January |
-3 |
|
February |
-1 |
|
March |
1 |
|
April |
3 |
If ![]() then
then
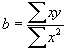
![]()
Example
|
|
Month |
Profit (y) |
Code (x) |
x2 |
xy |
|
|
1 |
31 |
-5 |
25 |
-155 |
|
|
2 |
40 |
-3 |
9 |
-120 |
|
|
3 |
30 |
-1 |
1 |
-30 |
|
|
4 |
34 |
1 |
1 |
34 |
|
|
5 |
25 |
3 |
9 |
75 |
|
|
6 |
20 |
5 |
25 |
100 |
|
Total |
21 |
180 |
0 |
70 |
-96 |
|
Average |
3.50 |
30.00 |
0.00 |
11.67 |
-16.00 |
b = -96/70 = -1.4
a = 30
Y = 30 - 1.4x
Forecasting error
Standard error of estimate
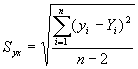 or
or
![]()
|
|
Month (x) |
Profit (y) |
xy |
y2 |
|
|
1 |
31 |
31 |
961 |
|
|
2 |
40 |
80 |
1600 |
|
|
3 |
30 |
90 |
900 |
|
|
4 |
34 |
136 |
1156 |
|
|
5 |
25 |
125 |
625 |
|
|
6 |
20 |
120 |
400 |
|
Total |
21 |
180 |
582 |
5642 |
![]() = 5.25
or
= 5.25
or
![]() = 5.25
= 5.25
|
Number of Syx |
Accuracy |
|
+/- 1 |
68% |
|
+/- 2 |
95.5% |
|
+/- 3 |
99.7% |
Formula review (pg.466)
Exercise:
Pg.471 Problems 17
Using Excel
1. Click Tools, Click Data Analysis
2. Choose Moving Average/Exponential Smoothing/Regression
|
Method |
Parameter |
Excel terminology |
Reminder |
|
N-mth Moving average |
N |
Interval |
Output range should be one cell lower than the input range |
|
Exponential Smoothing |
1-a |
Damping factor |
Output range should be at the same row as the input range |
|
Regression |
a b |
Intercept X variable or Label |
Label should be checked if you include the column heading in your input ranges |