- Critical Path Method (CPM)
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
Project -- a series of related jobs direct towards some major output and require a significant amount of time to perform
Project Management -- plan, direct, and control resources to meet the technical, cost, and time constraints of the project
An example
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
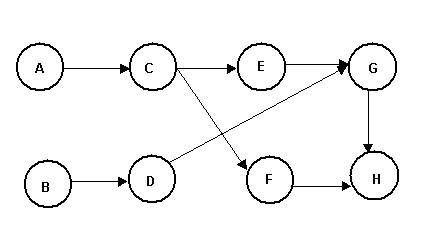
CPM -- single time estimate for each activity
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PERT -- 3 time estimates for each activity:
Optimistic time: a
Most likely time: m
Pessimistic time: b
![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earliest start time (ES) = max (EF of predecessors)
Latest start time (LS)
Earliest finish time (EF)
Latest finish time (LF) = min (LS of successors)
Slack = LS - ES or LF - EF
Critical path: activities that have zero slack
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total project completion time = sum of times of activities on the critical path
Pg. 81 problems 5, 6
Exercises
Pg.81 Problems 2, 3, 7, 9