Techniques
Morris water maze
This technique is used to test animals' abilities to learn and recall the location of a platform hidden under the surface of the water. The animal (rat or mouse) swims around the pool and maps the space around the maze. The pool is virtually divided in four quadrants and a camera tracks the animal’s location. After several training trials the animal is able to find the platform by using a set of cues placed on the walls surrounding the pool (black and white triangle and stripes in the picture). We are studying the impact of a long-term high fat diet on cognition using the Morris water maze.
Avoidance
This setup uses a shuttle box with 2 compartments (a light and a dark side) to monitor an animal’s recall ability. Training teaches the animal to associate a conditioning stimulus (mild shock) with a compartment. Successful training results in an animal leaving the compartment prior to the onset of the stimulus. We are studying the impact of a long-term high fat diet on cognition using the active avoidance setup.
Intracellular recording with simultaneous Calcium and Glucose imaging
We use sharp electrodes to impale individual neurons from area CA1 of the hippocampus. This allows use to monitor physiological responses to synaptic activation as well as to deliver fluorescent calcium and/or glucose indicators inside the cells. We are able to simultaneously record the physiology and to monitor the calcium status in neurons from young and aged animals. Using this type of technique we were the first to show enhanced calcium levels in hippocampal cells from aged animals during activation. We are currently investigating the actions of insulin in neurons from young and aged animals.
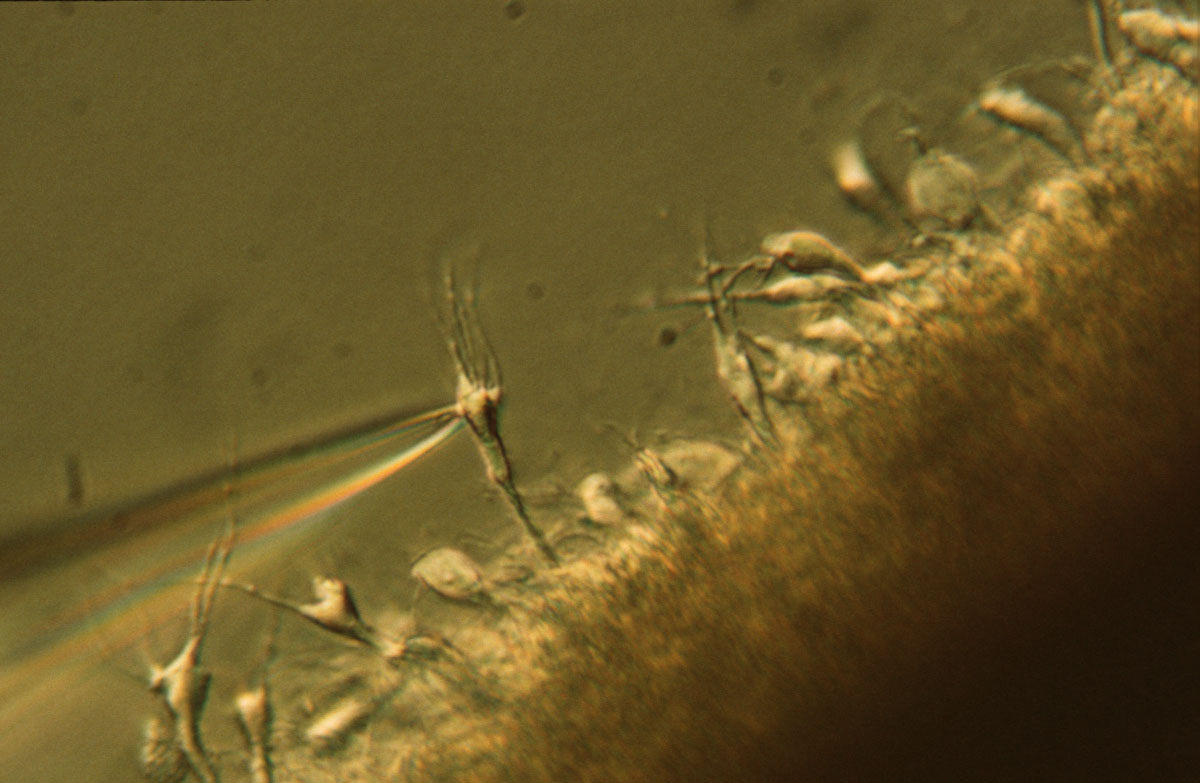
Zipper preparation
In this preparation, the hippocampal slice is mildly dissociated to reveal exposed single pyramidal neurons. Cell-attached patch clamping techniques are then used to record from single channels. We typically record from voltage-gated calcium channels and have shown that the density of the L-type voltage-gated calcium channels is increased on the membrane of aged neurons. We have recently finished a study investigating L-type channel density on the membrane of 2xTg-AD animals.
LTP setup
We use the extracellular recording technique to monitor synaptic responses in populations of neurons. This setup monitors dendritic or somatic field responses and allows us to determine synaptic strength within the hippocampus of young and aged animals. Ongoing study is monitoring the impact of baseline synaptic strength on LTP induction.
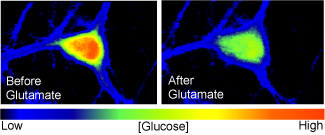
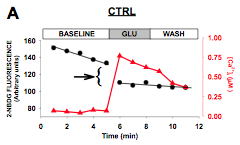
Glucose utilization measures
We use a fluorescent glucose analog (2-NBDG) to measure glucose utilization in live cells and astrocytes. Once inside the cell 2-NBDG looses its fluorescence proportionally with the activation of glycolysis. Measuring this decrease we were able to directly monitor glycolytic rate (Pancani et al. 2011).
Other techniques
We also use mixed hippocampal cultures of neurons and glia to determine glucose status in the two cell types. Other techniques include immunocytochemistry/ immunohistochemistry, Western blot, Elisa, microarray analyses, and other molecular approaches.